Systematic characterization of BAF mutations explains intra-complex synthetic lethalities
Supplementary Website
Study overview
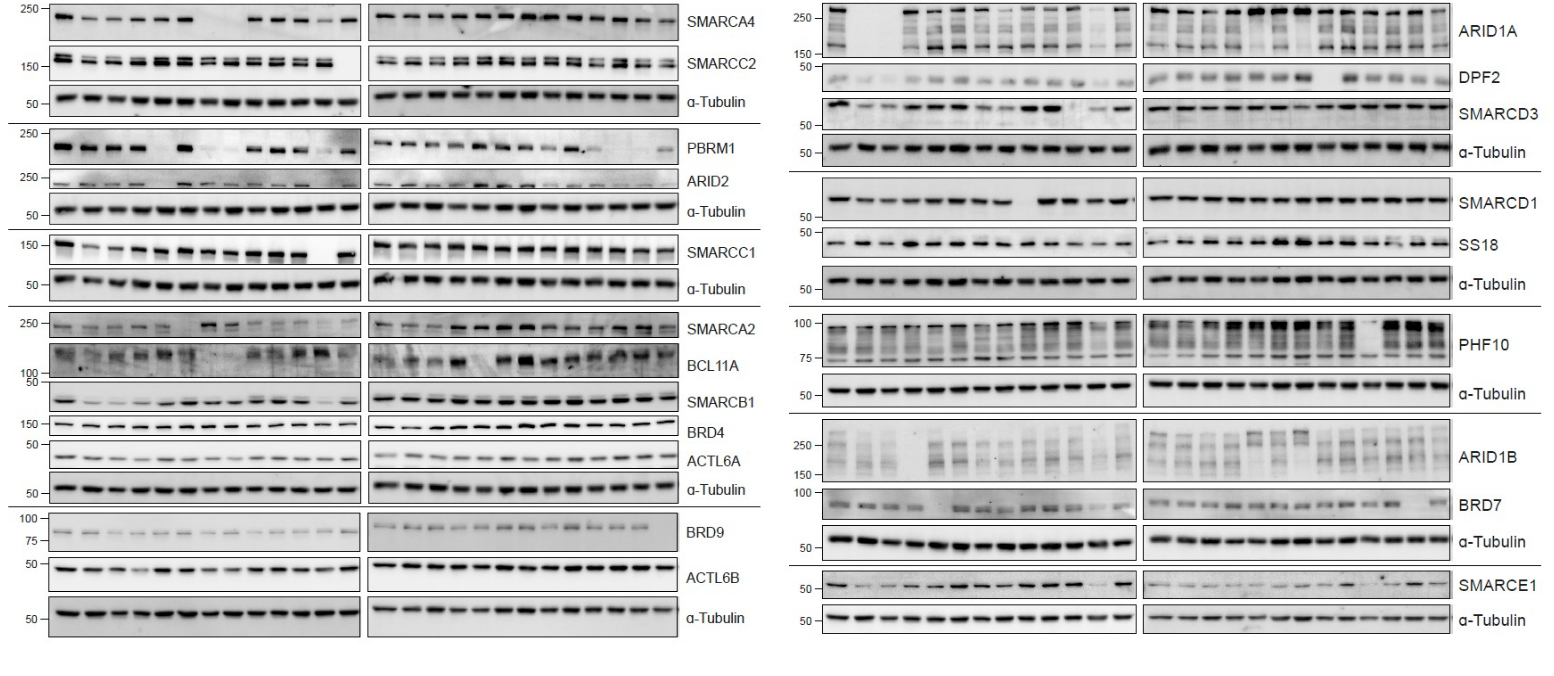
Arrayed knockout of BAF complex subunits
CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of BAF complex subunits in an arrayed format in isogenic haploid cell lines is throughly validated at protein and transcriptional level.
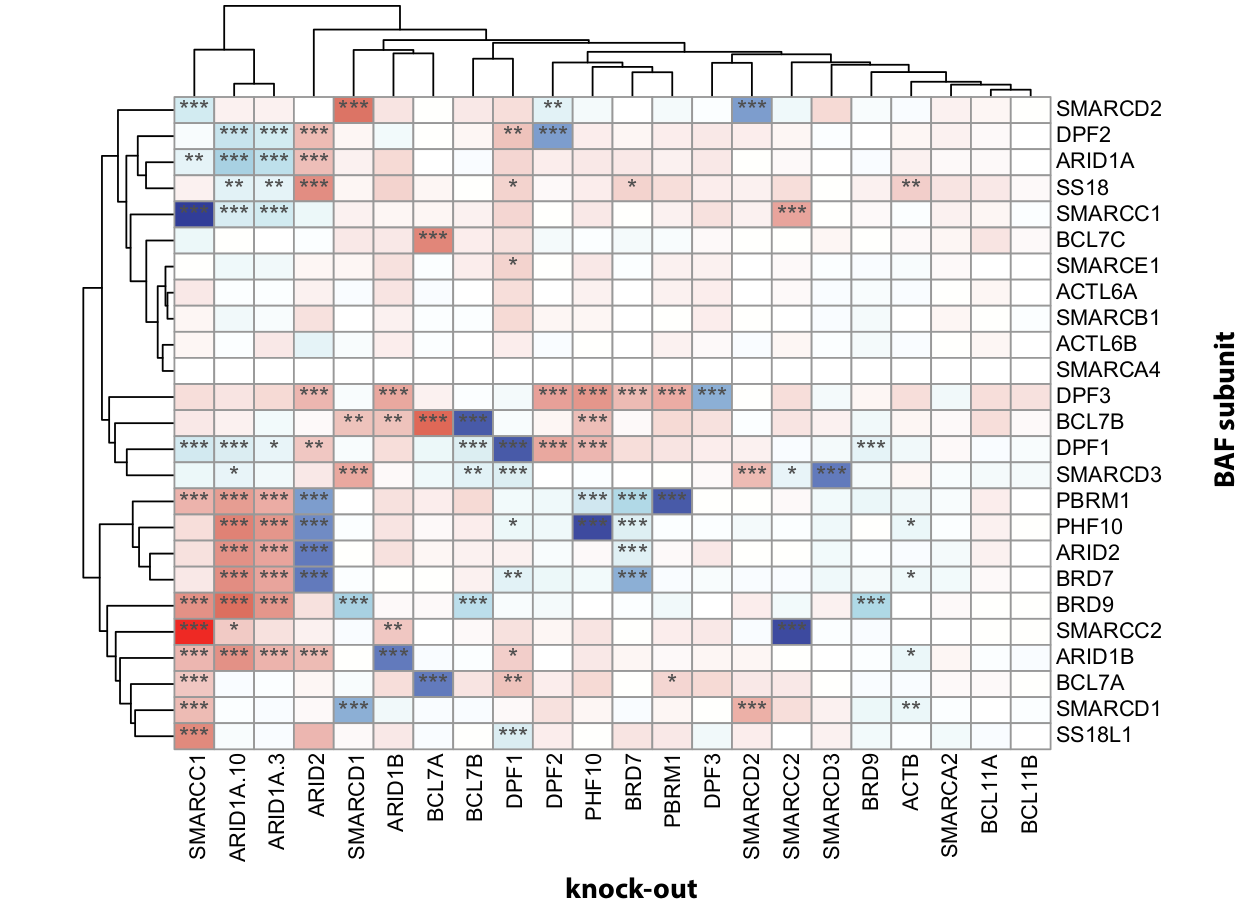
Mapping of BAF complex composition
Immunoprecipitation of BAF complex subunits followed by mass spectrometry (IP-MS) reveals complex composition changes upon loss of individual subunits.
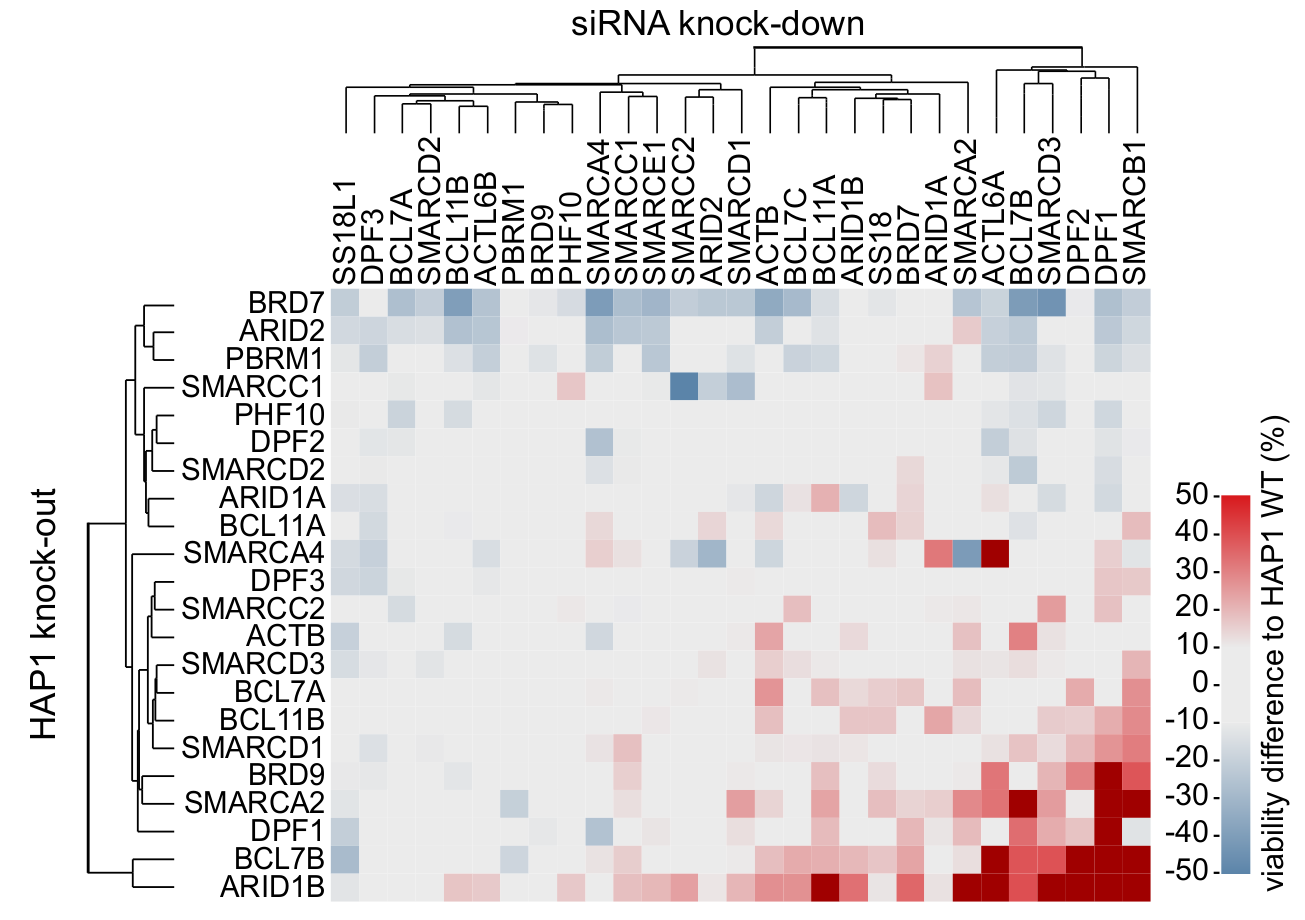
Synthetic interactions between BAF complex subunits
siRNA screen reveals intra-complex synthetic lethality interactions.
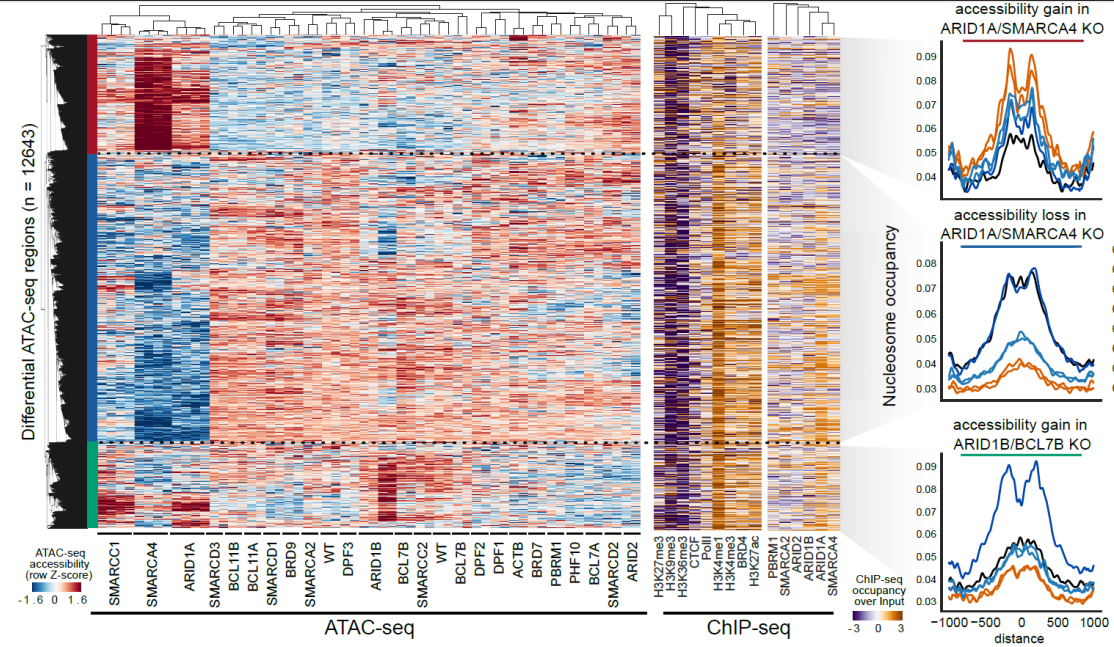
Regulatory interrogation of BAF complex subunit function
Chromatin accessibility changes of cells knockout for each subunit of the BAF complex reveal major functional subunits.
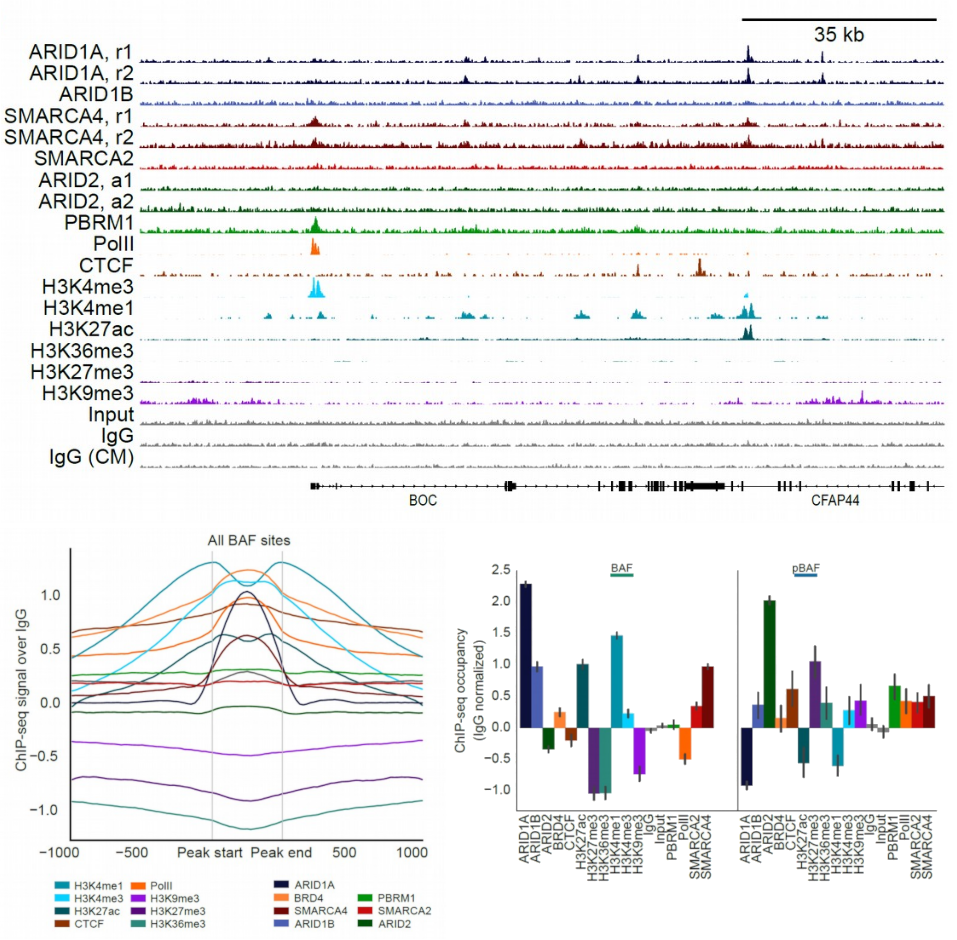
Extent and context of BAF complex chromatin binding revealed by ChIP-seq
Immunoprecipitation of key BAF complex subunits followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) reveals the breadth of complex binding to chromatin. ChIP-seq allows discovery of BAF-specific and pBAF-specific binding to chromatin. Comprehensive ChIP-seq for histone modifications reveals the chromatin context and likely functions of both complexes.
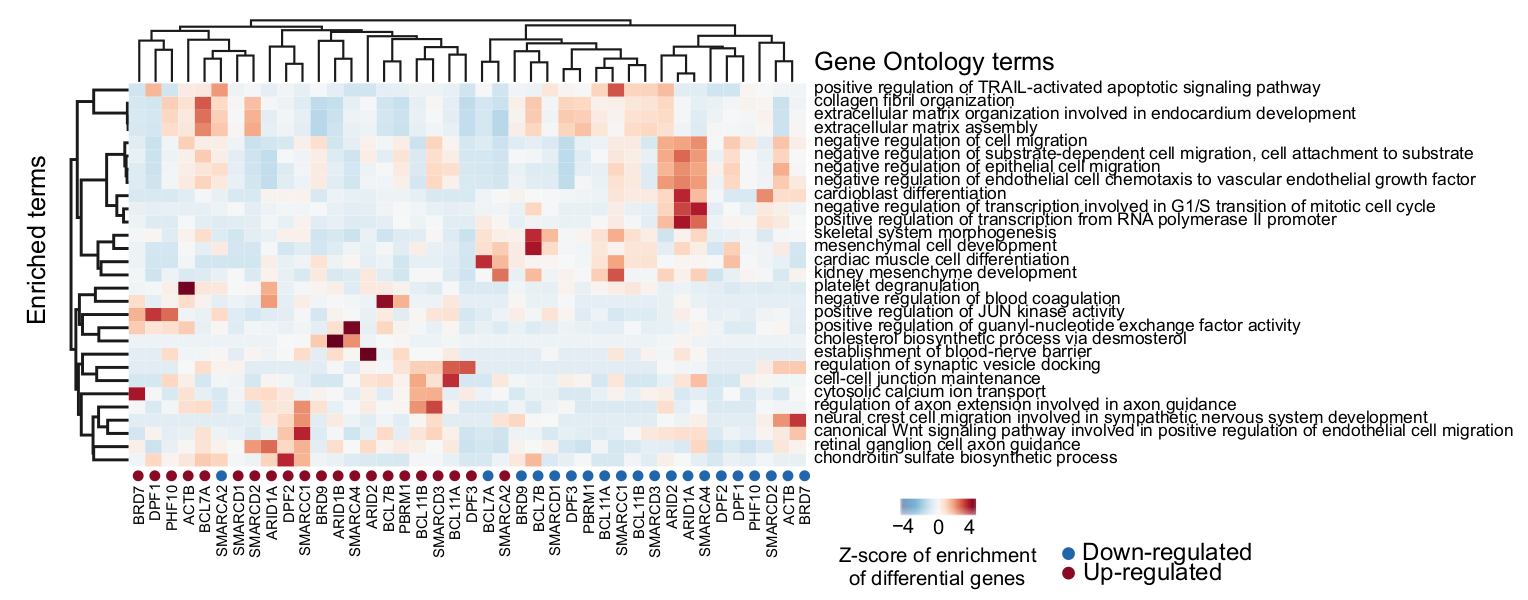
Transcriptional interrogation of BAF complex subunit function
Transcriptome profiling in all knockout cells reveals downstream effects upon individual subunit loss.
Genome browser tracks
We performed chromatin accessibility mapping by ATAC-seq, chromatin binding mapping by ChIP-seq and transcriptome quantification by RNA-seq on cell lines with single knockout of a BAF complex member.
The following genome browser tracks provide genome-wide maps of the effect of BAF complex mutation:
- Click here to add the track hub to UCSC Genome Browser.
- Click here to add the tracks to a local IGV Genome Browser session (please launch IGV first, e.g. via this URL).
Data
This section provides access to raw data and analysis results underlying the presented analysis of the BAF complex.
| Name | Description and link |
|---|---|
| Raw and processed NGS data |
GEO SuperSeries accession: GSE108390
GEO Series on ATAC-seq data: GSE108386 GEO Series on ChIP-seq data: GSE108387 GEO Series on RNA-seq data: GSE108398 |
| Protein-protein interaction of BAF complex subunits |
Comparison of IP-MS abundances between WT and knockout backgrounds: SMARCA4 IP, replicate 1, SMARCA4 IP, replicate 2; ARID1A IP, replicate 1, ARID1A IP, replicate 2 |
| Structural analysis of BAF complex |
Input files for structural analysis of BAF complex: SMARCA4 IP data, SMARCA4 IP p-values; ARID1A IP data, ARID1A IP p-values |
| Chromatin accessiblity of BAF complex subunit knockout cells |
Read count quantification of chromatin accessiblity signal in all samples: download here Normalized quantification of chromatin accessiblity signal in all samples: download here Coefficients of change in chromatin accessibility in knockout cells compared to WT: download here |
| Binding of BAF complex subunits to chromatin |
Read count quantification of ChIP-seq signal in all samples: download here Normalized quantification of ChIP-seq signal in all samples: download here BAF- and pBAF-specific bound regions: BAF-specific; pBAF-specific |
| Transcriptome of BAF complex subunits |
Read count quantification of RNA-seq signal in all samples at transcript level: download here Read count quantification of RNA-seq signal in all samples at gene level: download here Normalized quantification of RNA-seq signal in all samples: at gene level download here Coefficients of change in RNA-seq signal in knockout cells compared to WT: download here |
| Synthetic interaction of BAF complex subunits |
Viability measurements of BAF complex knock-out cell lines upon knock-down of additional subunits: download here |
Software
To foster reproducibility and facilitate reuse, the source code underlying the analysis is contained in a Git repository at Github.
Citation
If you use these data in your research, please cite:
Sandra Schick, André F. Rendeiro, Kathrin Runggatscher, Anna Ringler, Bernd Boidol, Melanie Hinkel, Peter Májek, Loan Vulliard, Thomas Penz, Katja Parapatics, Christian Schmidl, Jörg Menche, Guido Boehmelt, Mark Petronczki, André Mueller, Christoph Bock, Stefan Kubicek (2019).
Systematic characterization of BAF mutations explains intra-complex synthetic lethalities.
Nature Genetics. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-019-0477-9